The Burning Agony of Shingles: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention


Those who have experienced the excruciating pain of a shingles know just how intense it can be! Furthermore, it can potentially lead to persistent nerve pain, encephalitis, visual impairment, and hearing loss as serious long-term effects.
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. After recovering from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the nerve cells of the body. As one ages or due to other factors, when the immune system weakens, the dormant virus can "awaken" and attack and damage the nervous system, leading to the development of shingles.
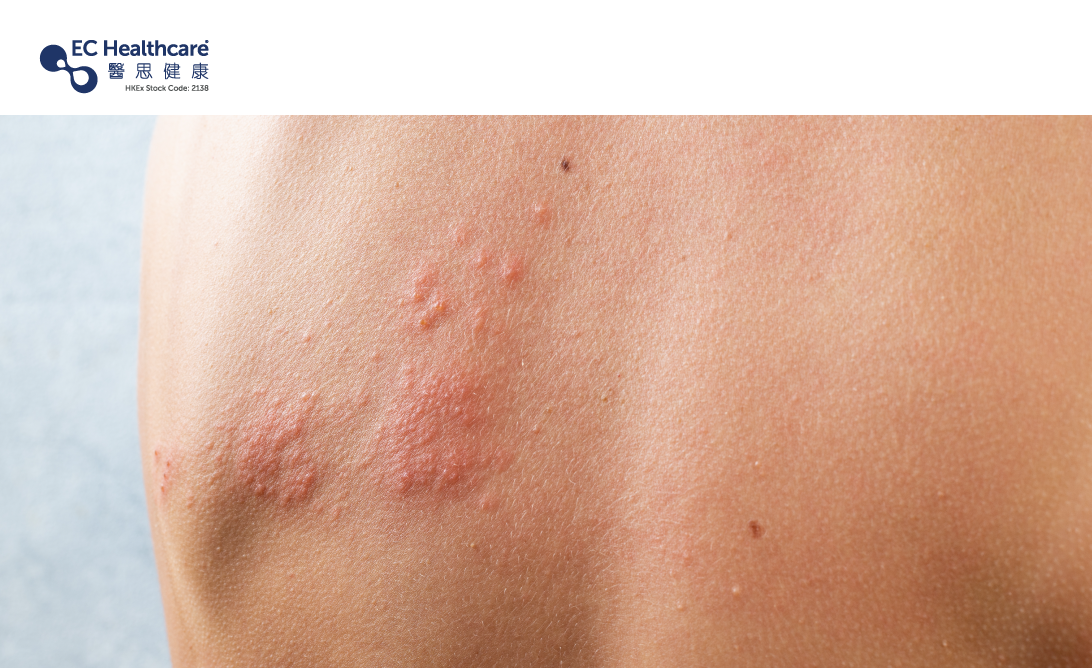
Patients with shingles may initially experience pain and tenderness in a specific area of the body. This is followed by the appearance of a red rash and subsequent sensations of numbness, tingling, burning, and even intense shooting pain, resembling electric shocks. These sensations are common symptoms experienced by individuals with shingles, but the severity can vary from person to person. The virus travels along the nerve pathways to the connected skin surface, resulting in the formation of a red rash. The rash is characterized by the presence of fluid-filled blisters, which typically spread in a band-like pattern depending on the distribution of the affected nerve fibers. These blisters can persist for up to 14 days, during which they may develop pus or become filled with blood before eventually drying up and forming scabs that will eventually fall off within 2 to 3 weeks. Failure to seek timely and appropriate medical treatment during the early stages of shingles can result in ongoing pain even after the blisters have healed and may lead to other complications.
Treatment and Prevention Methods
Currently, antiviral medications can shorten the healing time for patients with shingles. It is most effective when taken within 3 to 5 days of the onset of symptoms. Therefore, it is crucial for patients to seek medical attention promptly and follow their doctor's instructions for medication in order to control the condition and minimize the risk of complications. In addition, patients should maintain a comfortable room temperature and keep the affected area of the skin clean and dry. They may apply soothing creams or take pain relievers as needed to alleviate itching and discomfort. Patients should also avoid contact with individuals who are immunocompromised, such as pregnant women and children, to prevent them from getting infected.
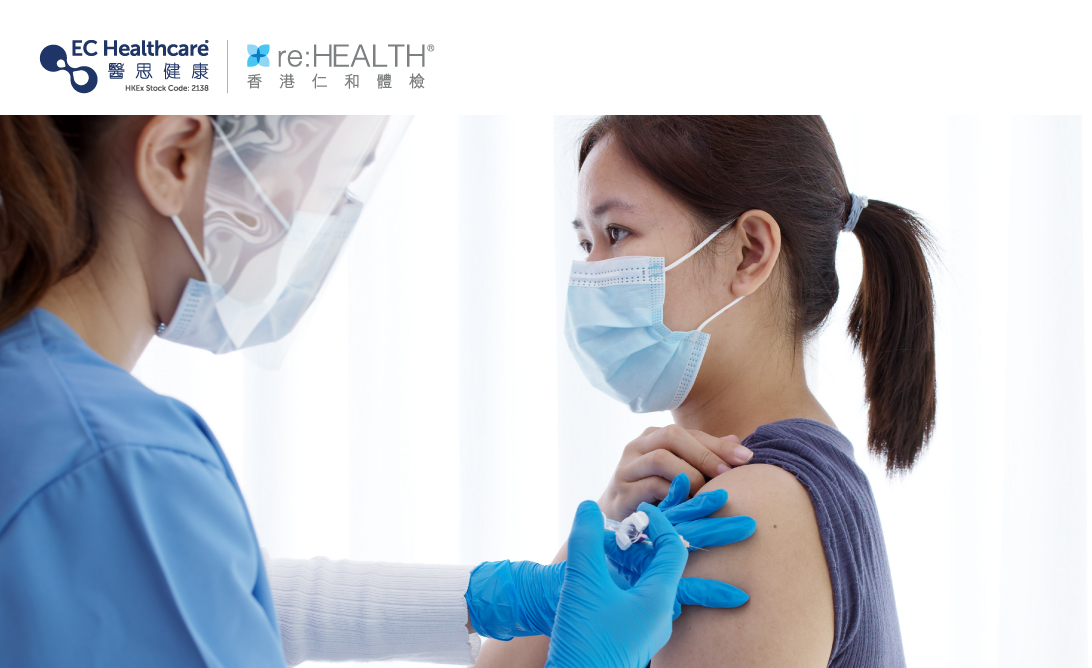
To prevent shingles, the medical community generally recommends vaccination, commonly known as the shingles vaccine, for individuals over the age of 50 who have had chickenpox in the past. While the vaccine does not guarantee complete prevention of shingles, it can significantly reduce the risk by up to 70%. Research has shown that although a small percentage of vaccinated individuals may still develop shingles, the onset time is shortened, the severity of pain is milder, and the risk of postherpetic neuralgia is lower.
As shingles can occur more than once, recovered individuals can receive the preventive vaccine. Some international guidelines recommend waiting for one year after the episode of shingles before getting vaccinated. However, it is important to note that the shingles vaccine is a live attenuated vaccine, meaning it contains weakened live varicella-zoster virus. There are several groups of individuals who are not suitable for vaccination, including those with compromised immune systems, individuals on high-dose corticosteroids, undergoing chemotherapy, or suffering from tuberculosis. It is advisable to consult a doctor before considering vaccination.
Related Brands